Health IT Adoption in Indian Hospitals: Current Trends & Prospects

Health IT adoption in Indian hospitals has emerged as a critical driver of healthcare transformation, enabling improved data management, clinical efficiency, and patient-centered care.
Traditionally, hospital operations in India relied heavily on paper-based records, fragmented data systems, and manual workflows, leading to inefficiencies, data loss, and limited continuity of care. The rapid growth of digital technologies, combined with policy-driven healthcare reforms, has accelerated the adoption of Health Information Technology (Health IT) within Indian hospitals.
Driven by national policy initiatives like the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) and recent investments in digital infrastructure, hospitals across India are increasingly leveraging digital tools such as Electronic Medical Records (EMRs), Hospital Information Systems (HIS), telemedicine platforms, and interoperable health networks.
This article focuses on the current trends in Health IT adoption in Indian hospitals, highlighting its benefits and future trajectory.
What is Health Information Technology (Health IT)?
Health Information Technology (Health IT) refers to the use of digital systems, software applications, and information infrastructure to collect, store, manage, exchange, and analyze health-related data across the healthcare ecosystem.
In hospitals and healthcare facilities, Health IT supports both clinical and administrative functions, helping to improve patient outcomes, streamline operations, and enhance data-driven decision-making.
In the Indian context, Health IT adoption in Indian hospitals has played a pivotal role in strengthening healthcare systems and advancing national digital health initiatives such as the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM).
The primary objectives of Health IT are to:
- Improve the quality and safety of patient care
- Enable timely access to accurate health information
- Enhance care coordination and continuity
- Increase operational efficiency in healthcare delivery
- Support patient engagement and empowerment
- Ensure secure, standardized, and interoperable health data exchange
Health IT Adoption in Indian Hospitals: Current Trends
Health IT adoption in Indian hospitals has accelerated significantly over the past decade, driven by national digital health policies, technological innovation, and evolving patient expectations. While adoption levels vary across regions and hospital types, several clear trends illustrate how hospitals are integrating digital technologies into routine healthcare delivery, some of which are
1. Adoption of Hospital Information Systems (HIS) and Digital Records
The adoption of Hospital Information Systems (HIS) and Electronic Medical Records/Electronic Health Records (EMR/EHR) in Indian hospitals has increased steadily over the past decade; however, the depth and maturity of implementation remain uneven across the healthcare system.
Mid-to-large hospitals, especially in urban and metropolitan areas, are more likely to have implemented HIS platforms.
Further, government incentive programs, digital health certification frameworks, and standardization efforts under ABDM are encouraging broader adoption.
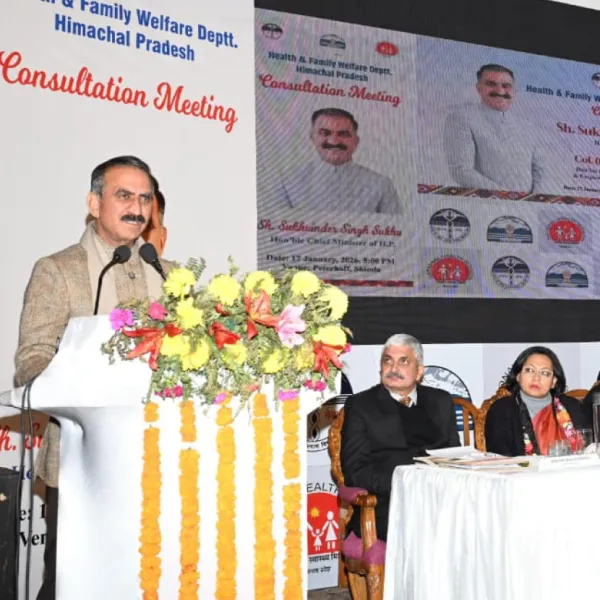
Government implementations like Delhi’s online OPD booking via HIMS showcase how HIS solutions are improving patient experiences and hospital efficiency.
2. Interoperability and Health Information Exchange
Interoperability is a defining trend in India’s Health IT landscape, driven by efforts to integrate diverse digital solutions into a unified national ecosystem. Initiatives such as the Unified Health Interface (UHI) and the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) aim to connect hospitals, telemedicine platforms, diagnostic services, and health registries through standardized digital protocols.
Improved interoperability enables hospitals to achieve several critical outcomes, such as seamless access to patient records, reduction in duplication of diagnostic tests and procedures, lowering costs and patient burden, and enhanced care coordination and continuity.
3. Telemedicine & Virtual Care
Telemedicine and virtual care adoption in Indian hospitals surged during the COVID-19 pandemic, and many hospitals have since integrated teleconsultation platforms into routine workflows to improve access to outpatient services, specialist care, and follow-ups, especially for patients in rural and underserved areas.
The issuance of national Telemedicine Practice Guidelines and E-Sanjeevani has further institutionalized remote care by providing legal and clinical clarity around virtual consultations, e-prescriptions, referrals, and continuity of care.
4. Data Analytics & AI-Driven Clinical Workflow
Hospitals are beginning to leverage digital data generated through Health IT systems for performance monitoring, quality improvement, and clinical decision support.
AI adoption in Indian healthcare IT is accelerating rapidly:
Hospitals and digital health companies are using AI for diagnostics, clinical decision support, and workflow automation (e.g., AI-powered document digitization, screening tools).
Government and private partners are deploying AI tools in screening and predictive analytics, including rural health programs and disease surveillance.
This trend reflects a broader shift from digitization to intelligent automation in healthcare operations and clinical support.
Benefits of Health IT Adoption in Indian Hospitals
Health IT adoption in Indian hospitals has generated significant benefits across clinical, administrative, and patient engagement domains. Some of the key benefits are-
1. Improved Quality and Safety of Patient Care by enabling accurate patient information and reducing clinical errors.
2. Enhanced Operational Efficiency by digitalizing and streamlining administrative workflows such as patient registration, billing, scheduling, etc., leading to faster service delivery and reduced operational costs.
3. Improved Care Coordination and Continuity through interoperable digital systems, which enable seamless sharing of patient information across departments and healthcare providers.
4. Expanded Access to Healthcare Services in remote areas through Telemedicine and virtual care platforms.
5. Health IT adoption in India has enabled data-driven clinical and managerial decisions through real-time data for care improvement and resource optimization.
6. Health IT enhances patient engagement and experience by providing digital access to records, improving transparency and trust.
Conclusion
Health IT adoption in Indian hospitals is transforming the healthcare landscape by improving efficiency, quality, and accessibility of care. National policies, digital infrastructure investments, and technological innovations are driving adoption, while trends such as telemedicine, interoperability, data analytics, and AI are shaping the future.
Despite the progress, challenges like infrastructure gaps and data standardization still persist. Addressing these challenges becomes essential to fully realize the benefits of digital healthcare and create a patient-centric, connected hospital ecosystem.
Stay tuned for more such updates on Digital Health News