How ABDM Enables Continuity of Care across Providers in India: A Comprehensive Study

In India’s fragmented healthcare system, the coordinated care system has historically been limited by a lack of interoperable systems and consolidated patient data. Improving clinical outcomes and healthcare efficiency largely depends upon how well a coordinated healthcare system ensures continuity of care, especially in systems where patients engage with several clinicians over time. To mitigate the obstacles caused by this fragmented healthcare structure, the India Governemnt launched the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) in 2021. By creating a nationwide digital health infrastructure that facilitates the easy, consent-based sharing of medical records amongst providers, the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) aims to overcome these obstacles and improve continuity of care.
This article examines how ABDM enables continuity of care across providers through interoperable digital infrastructure, standardized structure, and a unified digital health system.
ABDM Overview
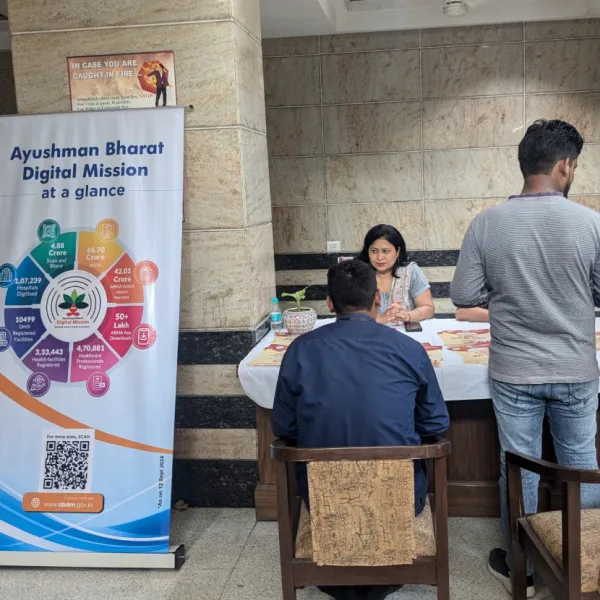
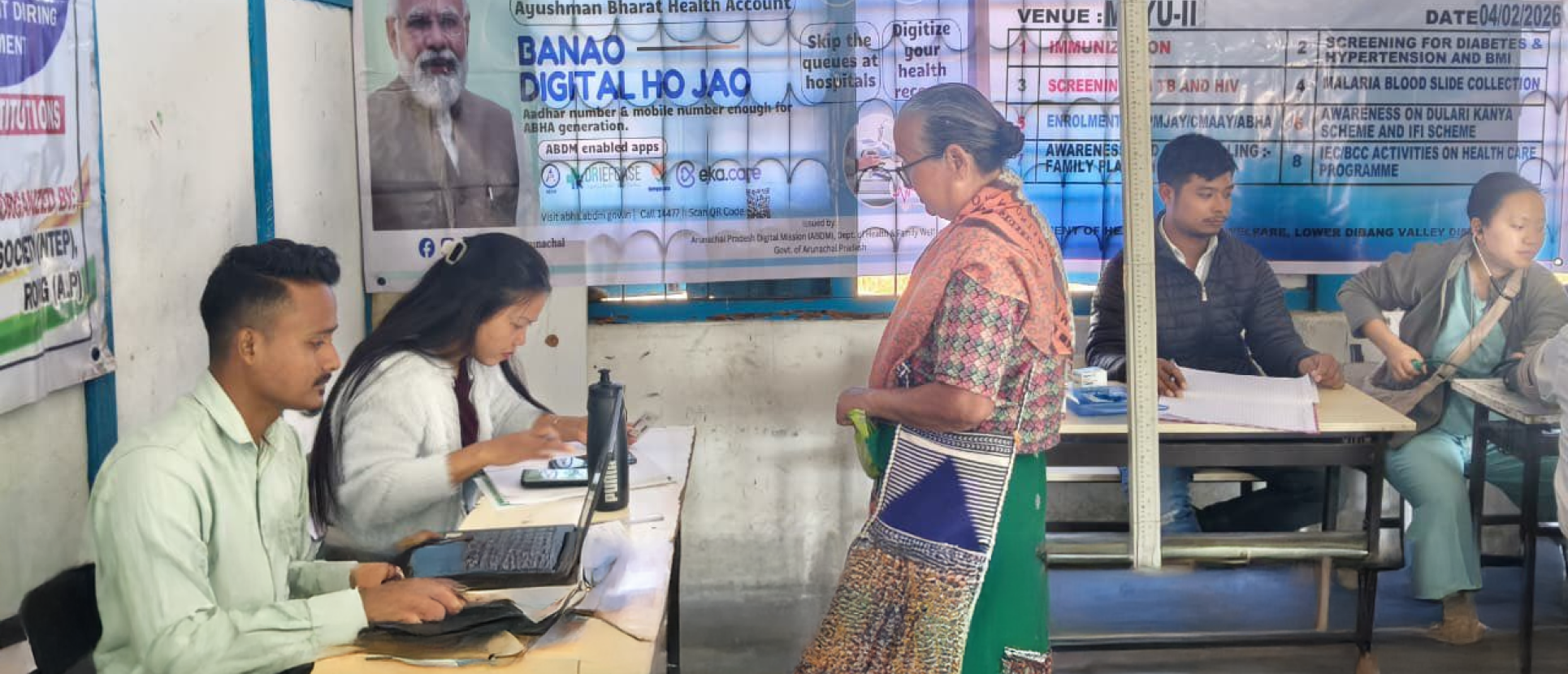
ABDM was launched in 2021 to create a unified digital system and is built as a federated digital ecosystem, guaranteeing flexibility, scalability, and data privacy. The healthcare initiative is built on key structural elements, such as the Ayushman Bharat Health Account (ABHA) number, which acts as a unique health identifier, the Health Facility Registry (HFR), and the Healthcare Professional Registry (HPR), which authenticate participating entities, and a consent manager framework that permits patient-controlled data sharing.
How ABDM Enables Continuity of Care
ABDM enables continuity of care by creating a patient-centric interoperable digital framework that allows health information to flow securely across providers and care settings. Central to the structure is the Ayushman Digital Bharat Account, which creates a permanent and lifelong health identity that connects medical records produced by various healthcare providers to a single person. As a result, care decisions can be made based on a thorough understanding of the patient's health journey rather than based on a single clinical encounter. This is made possible by the construction of longitudinal health records that compile clinical history, diagnostic reports, prescriptions, and discharge summaries across time.
ABDM uses nationally accepted data formats and established application programming interfaces (APIs) to enable smooth data interchange across public and commercial healthcare systems through its interoperable digital infrastructure. The interoperability and data exchange are enabled through three gateways, such as the Health Information Consent Manager (HIE-CM), the National Health Claims Exchange (NHCX), and the Unified Health Interface (UHI), which together support seamless, secure, and consent-based digital health services.
The consent-based data sharing system places the patients at the center, which provides them with clear and auditable control over who can access their health information. This enhanced cross-provider clinical visibility allows clinicians to access prior treatment histories during consultations and referrals, reducing information gaps, unnecessary repeated investigations, and delays during transitions of care across primary, secondary, and tertiary facilities.
Further, ABDM improves continuity of care for chronic and long-term conditions by facilitating seamless data sharing, continuous monitoring, follow-up, and enhanced coordinated treatment planning. Additionally, the integration of pharmacy and diagnostic data with clinical encounters improves medication adherence and treatment continuity.
Furthermore, the portability of digital health records facilitates patient mobility beyond geographical boundaries, guaranteeing continuous care even when people seek treatment in several states, towns, or healthcare networks. By facilitating the use of aggregated and anonymized health data for public health planning, illness surveillance, and the successful execution of national health programs, the mission also promotes population health and programmatic continuity at the system level.
Conclusion
The Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission represents a transformative shift in India’s approach to healthcare delivery by addressing fragmentation and enabling continuity of care across providers. Through unique health identifiers, interoperable infrastructure, and consent-driven data sharing, ABDM supports coordinated, longitudinal, and patient-centered care. While challenges related to adoption, digital literacy, and data governance remain, ABDM lays a strong foundation for a more integrated and efficient healthcare system in India.
Stay tuned for more such updates on Digital Health News